If I Pick Prime Numbers For My Security, How Fast Will I Find Them, and How Safe Are They?

If I Pick Prime Numbers For My Security, How Fast Will I Find Them, and How Safe Are They?
Many of our public key methods rely on prime numbers, as they have wonderful properties, including a way of performing mathematical operations on numbers, but constrain them with a finite field (and where our maximum number is the prime number less one). The difficulty in RSA, for example, is to factorize the value of N into the two prime numbers which created N. If these are found, we can easily find out the decryption key associated with the encryption key [here].
The Greek mathematician Euclid showed that there is no “largest” prime number, and we can go onto infinity and never find the last prime.
So if we pick a prime number of a certain size, how do we know how many prime numbers that an intruder has to search through to find the one (or ones) we have used? If we select a small value, such as between 0 and 15 (4 bits), it is not going to be difficult, as the prime numbers will be:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17 and 19
But if we pick 10⁵⁰ how can we estimate the number of prime numbers there are. Well in cryptography we can use the pi(x), function to estimate the number of primes between 0 and x.
One of the simplest methods of calculating π(x) is to generate them and count. The following code does a sieve derived from a method defined by the Greek mathematician Eratosthenes. With this we filtering out multiples of each prime [here]:
One of the methods used is to calculate the prime counting function π(x) using Schoenfeld’s inequality:

One method which can be used to estimate the number of prime numbers is the Riemann R function. This is a smooth approximation for π(x). The function is defined using the rapidly convergent Gram series:
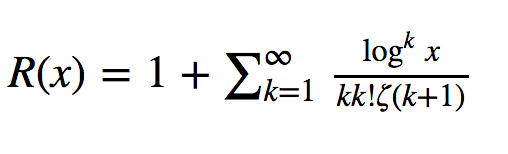
A sample run is [here]:
Range from 0 to 1000000
Estimation of primes: 78498
Possibility of finding prime (%): 7.8498
----- Using Riemannr method to estimate
Estimation is: 78527
Range Est number of primes
10^ 1 4
10^ 2 25
10^ 3 168
10^ 4 1226
10^ 5 9587
10^ 6 78527
10^ 7 664667
10^ 8 5761551
10^ 9 50847455
10^ 10 455050683
10^ 11 4118052494
10^ 12 37607910542
10^ 13 346065531065
10^ 14 3204941731601
10^ 15 29844570495886
10^ 16 279238341360977
10^ 17 2623557157055978
10^ 18 24739954284239496
10^ 19 234057667300228928
10^ 20 2220819602556027136
10^ 21 21127269485932298240
10^ 22 201467286689188773888
10^ 23 1925320391607837261824
10^ 24 18435599767347541311488
10^ 25 176846309399141946490880
10^ 26 1699246750872419937812480
10^ 27 16352460426841662628560896
10^ 28 157589269275973244548022272
10^ 29 1520698109714271704874745856
10^ 30 14692398897720432138328735744
In this case, if we were to select a number at random between 0 and 1,000,000, the probability that we will find a prime number is 7.84%. Often when we pick a random prime number, we start with a random number, and then keep subtracting one from the value, and testing it, until we find a prime.
And so, if our attacker can tries 1 billion prime numbers per second, then if we select a prime number in the range of 10¹⁵, it will take around 29,800 seconds — or just eight hours — to try them all. So we need to make sure that the prime number size is large enough, so that an intruder will have too many prime numbers to find in order to crack the keys.
If you are interested 10³⁰ is equivalent to 99 bits. Normally with RSA we use 2,048, so there’s lots of primes that an intruder would have to search through. Here is my little simple Python code that coverts 10³⁰ to bits:
>>> import math
>>> y=10**30
>>> print math.log10(y)/math.log10(2)
99.6578428466
Conclusions
RSA works because of the difficulty in finding two prime numbers which make n, and which is a hard task for an adversary. Unfortunately if that adversary has a quantum computer the task becomes a whole lots easier. So, for just now, RSA works, but perhaps not in the future.