Your Computer Monitor Could Be Leaking Sound Information …

Your Computer Monitor Could Be Leaking Sound Information …
Recently, I found that my Cisco WebEx agent was seeking out other devices in my home, and while most software packages will broadcast onto a network, this program uses acoustics [here]:

Overall, it feels rather strange for my computer to seek out other devices using ultrasound methods — especially as I can’t remember it asking me for this. But, some of the coolest work around relates to the usage of side channel analysis to discover secrets, and so I am currently reading this paper [here][1]:

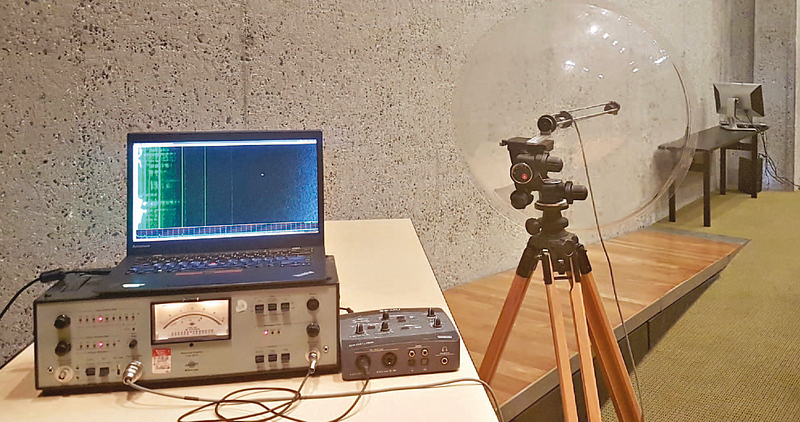
Experimental setup
The research work aims to pick up the vibrations that are caused when a computer screen refreshes its content. It involves using a directional acoustic receiver. The attacks identified were:
- Close-range and at-distance attacks. With this, an attacker could listen in on the audio feeds from a call, and pick up the contents of the screen for this. The experimental setup for this is should in Figure 1.
- Phone attacks. With this, a smart phone is used to monitor the video content through transmitted audio. The experimental setup for this is should in Figure 2. In order to detect the acoustic from the screen, the research team sourced a zebra pattern on the screen, and then tried to pick up the contents of the screen from five meters away.
- VoIP attacker. This picks up audio from a VoIP call.
- Virtual assistant attack. This picks up audio from virtual assistants. The experimental setup for this is shown in Figure 3.



Results
The results can be summarised:
- For on-screen keyboard snooping, the researchers use a CNN classifier method to learn the patterns involved. For close and smart phone detection, the results showed that the classifier achieved 100% accuracy.
- For text extraction, the researchers focused on picking out words from the screen. The accuracy of detection varied from 88% to 98%, apart from the last character which only gained a 75% accuracy.
- For Website distinguishing, the researchers aimed to find the Web sites that a target is using. Unfortunately, the results for this one were inconclusive.
- For cross-screen attacks, the researchers focused on distingishing between multiple screens that a user was using. The results for this differentiation is given in Figure 4.
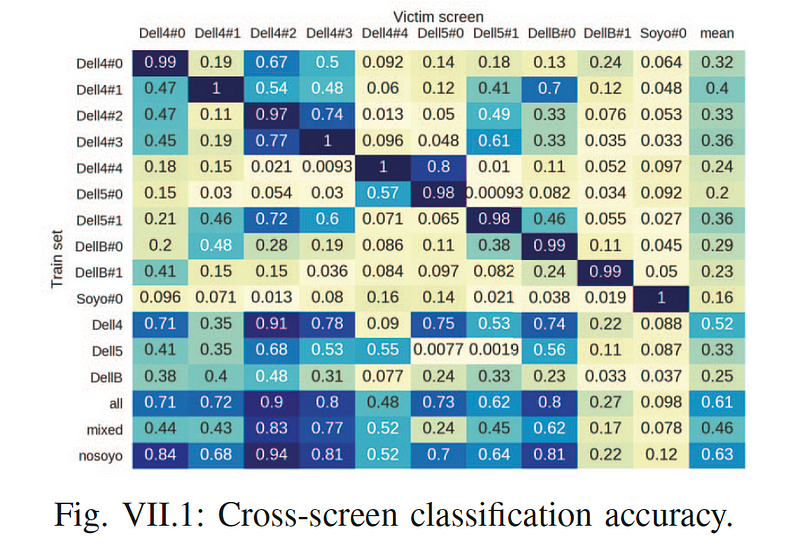
Conclusions
If you can, go read the paper [here]. The thought that someone may be watching your steps through side channels, is a worry, especially where you may be entering your PIN or password on an on-screen keyboard.
Reference
[1] Genkin, Daniel, et al. “Synesthesia: Detecting screen content via remote acoustic side channels.” 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2019. [here]